Stable cell line construction with point mutation
Point mutations refer to the introduction of single nucleotide mutations at specific sites using CRISPR/Cas9 or other gene editing technologies, including base substitutions, insertions, or deletions. Point mutation cells can be used for gene function research, disease mechanism research, drug development, and evolutionary studies. See details on the Liman official account: Technical Feature | Common Application Scenarios of Gene Point Mutation Cell Lines【Collection】
However, successfully constructing a point mutation cell line is not simple. Liman Biology provides one-on-one customized services, designing the most suitable technical solutions based on customer needs to make your scientific research more efficient. Liman provides in vitro gene point mutation cell line construction services for eukaryotic cells. For this service, the Liman team will regularly update Q&A to better serve our customers. The Q&A【2411 version】is as follows:
1. What is the principle of the method used in Liman's point mutation service?
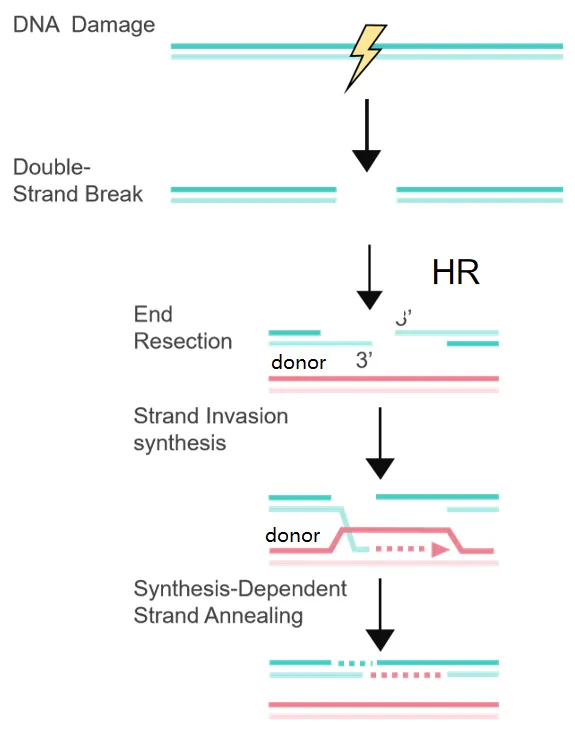
The theoretical basis for constructing a cell point mutation model is homologous recombination repair. When double-stranded genomic DNA is broken due to external factors, the existing DNA repair mechanisms in the cell are activated to repair the broken double-stranded DNA. Depending on the repair method, it can be divided into homologous recombination repair (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). Homologous recombination repair (HR) refers to the perfect repair of DNA using homologous DNA sequences as a template during repair. Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) refers to the direct reconnection of the broken ends of DNA by related proteins in the cell, which may randomly introduce or delete a certain number of bases. By using the appropriate method to promote homologous recombination repair while introducing donor DNA containing the specified mutation, point editing of the target DNA can be achieved.
2. What information do I need to provide when consulting about point mutation needs?
You only need to provide the cell name, target Gene Symbol, and point mutation site information (for example: A549 cell point mutation of the 42nd amino acid of gene A, AAG mutated to AGG).
3. What types of point mutations do you perform?
Generally, all mutation types can be performed. Theoretically, within 30 bases, it belongs to the category of point mutations, including but not limited to missense mutations, synonymous mutations, and nonsense mutations, depending on the customer's needs.
4. What is the success rate of point mutations?
The success rate of point mutations is related to the cells and target points. When performing double-stranded DNA repair, the probability of homologous recombination is between 0.3% and 5%. Liman Biology has developed a unique method that can significantly increase the probability of homologous recombination repair (8-12%) in most cell lines. Combined with our automated single-clone isolation and sequencing analysis, the success rate of isolating single clones can be effectively improved.
5. What are the advantages of your point mutation services?
①Technical Advantages: For point mutation cells constructed using the above method, no additional reporter or resistance genes are introduced, which can minimize the impact on non-edited sites of the genome.
②Scheme Design: A gene editing team with more than 10 years of overseas research experience carefully optimizes and designs point mutation schemes, comprehensively considering the PAM region of sgRNA cutting, cutting specificity, the position and length of the donor sequence and modification, and the binding site of sequencing verification primers and other details.
③Transfection Advantages: Liman Biology has successfully edited more than 3000 cells, ensuring transfection efficiency and significantly improving the success rate of point mutations.
④Single Clone Screening: Liman Biology has achieved automated single-clone plating and selection. Through efficient single-clone sequencing, the editing success rate is greatly improved.
6. What is the cycle time for point mutations?
The cycle time for cell line development is related to the cell doubling time. The shorter the doubling time, the faster the development cycle. For example, if the cell doubling time is within 24 hours, the cycle time to obtain a point mutation cell line is 8-10 weeks, and the cycle time will be adjusted according to the cell doubling time.
7. What are the deliverables for point mutations?
①Cell Line: Point mutation positive single-clone cell line. Our company provides various cell delivery methods, such as simultaneous delivery of WT cells and point mutation cells, and customers can choose cryopreservation tubes or T25 live cells.
②Point Mutation Cell Line Construction Report: Detailed description of cell culture methods, cell construction process, Sanger sequencing report, and original data. Our company provides all after-sales services related to the cell line, including ensuring that the cells are free of contamination, the genotype is stable during passage, ensuring that customers can successfully revive the cells, and providing services such as Sanger verification data analysis after multiple passages.

