Technology Topics | Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS): A New Frontier in Modern Biomedicine]
2024-08-04
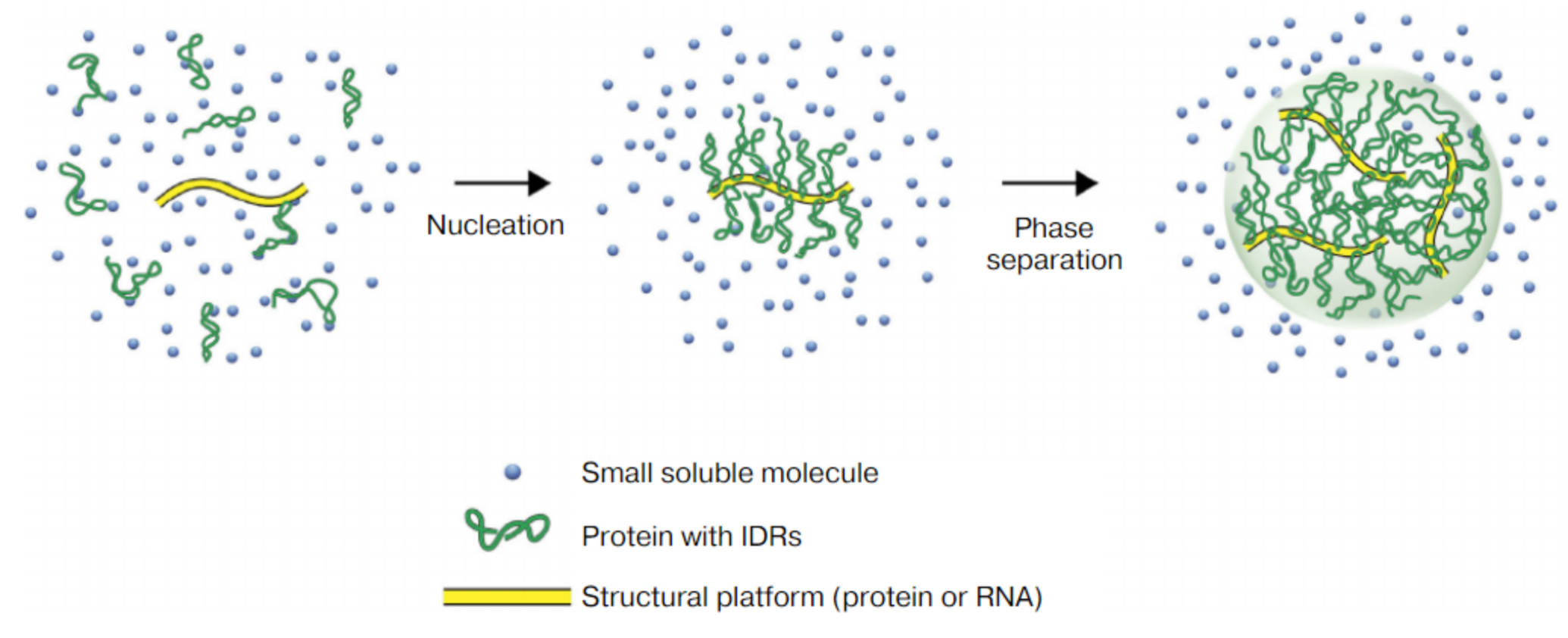
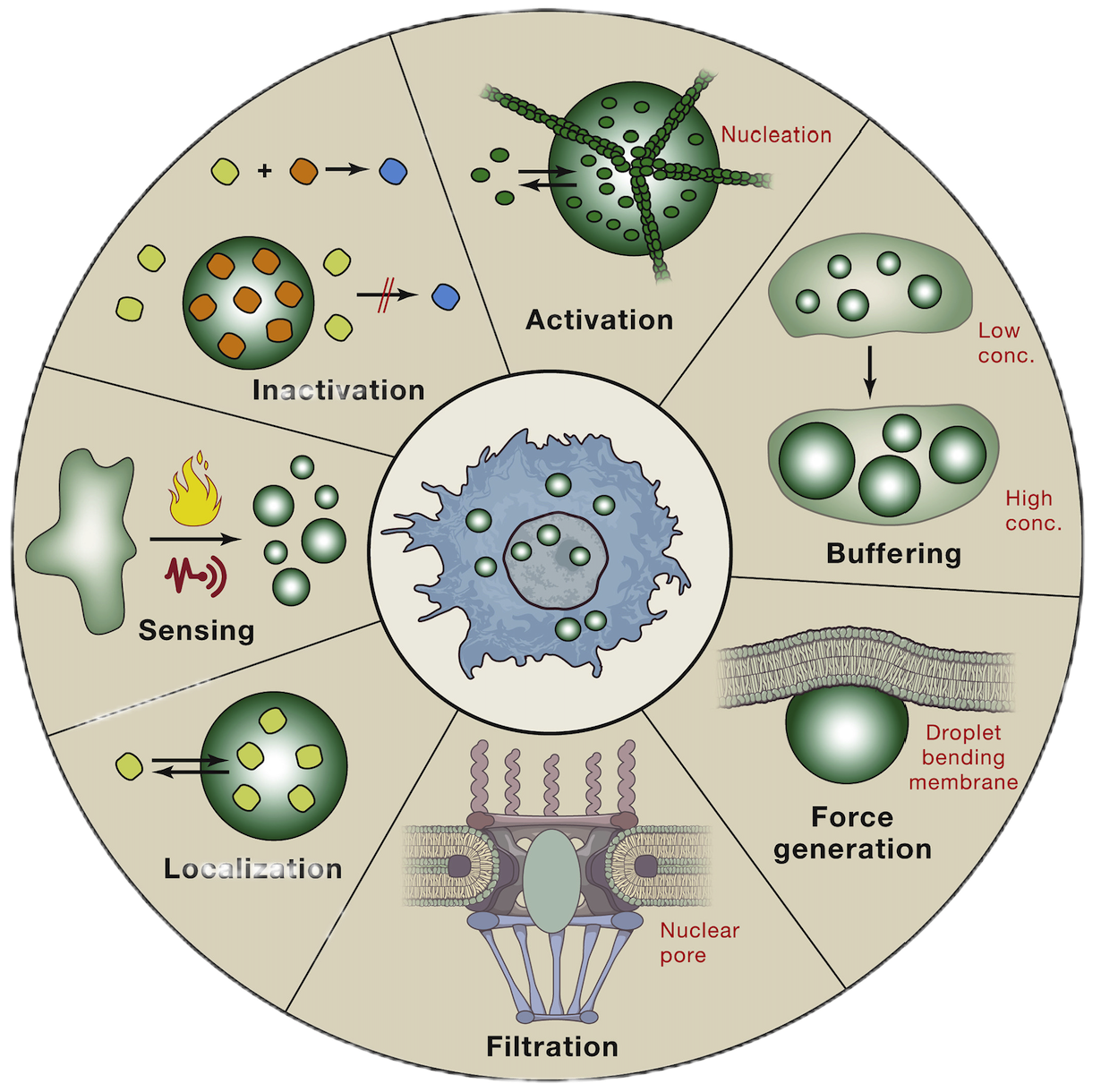
Liquid-liquid phase separation (Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation, LLPS) refers to the formation of phase separation droplets with different components and properties through the interaction of certain biological macromolecules (such as proteins and RNA) in cells [1]. These droplets are similar to the isolated state of oil droplets in water, forming a unique substructure within the cell. The phenomenon of liquid-liquid phase separation is widespread in the nucleus, cytoplasm and organelles, and is an important part of many cellular processes.
2.Study on phase separation in tumor
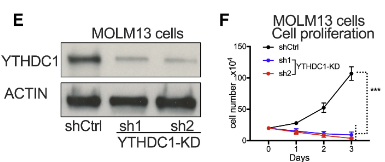
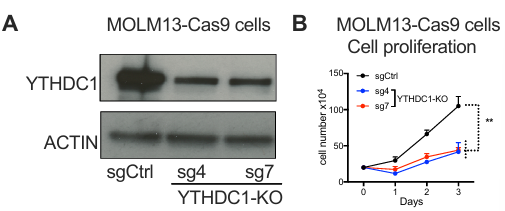
2)CRISPR/Cas9 gene knock-in for endogenous YTHDC1 plus EGFP tagIt is proved that YTHDC1 protein is separated by liquid-liquid phase in vivo and in vitro.
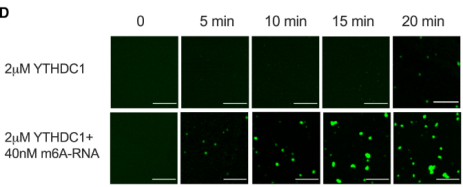
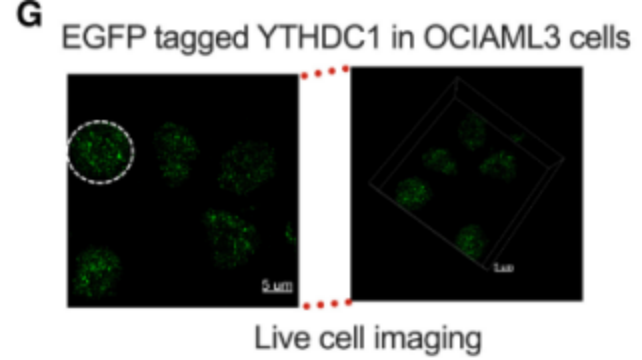
3)Point mutation or fragment knockoutCharacterization of the IDR domain in YTHDC1 is critical for LLPS in cells.
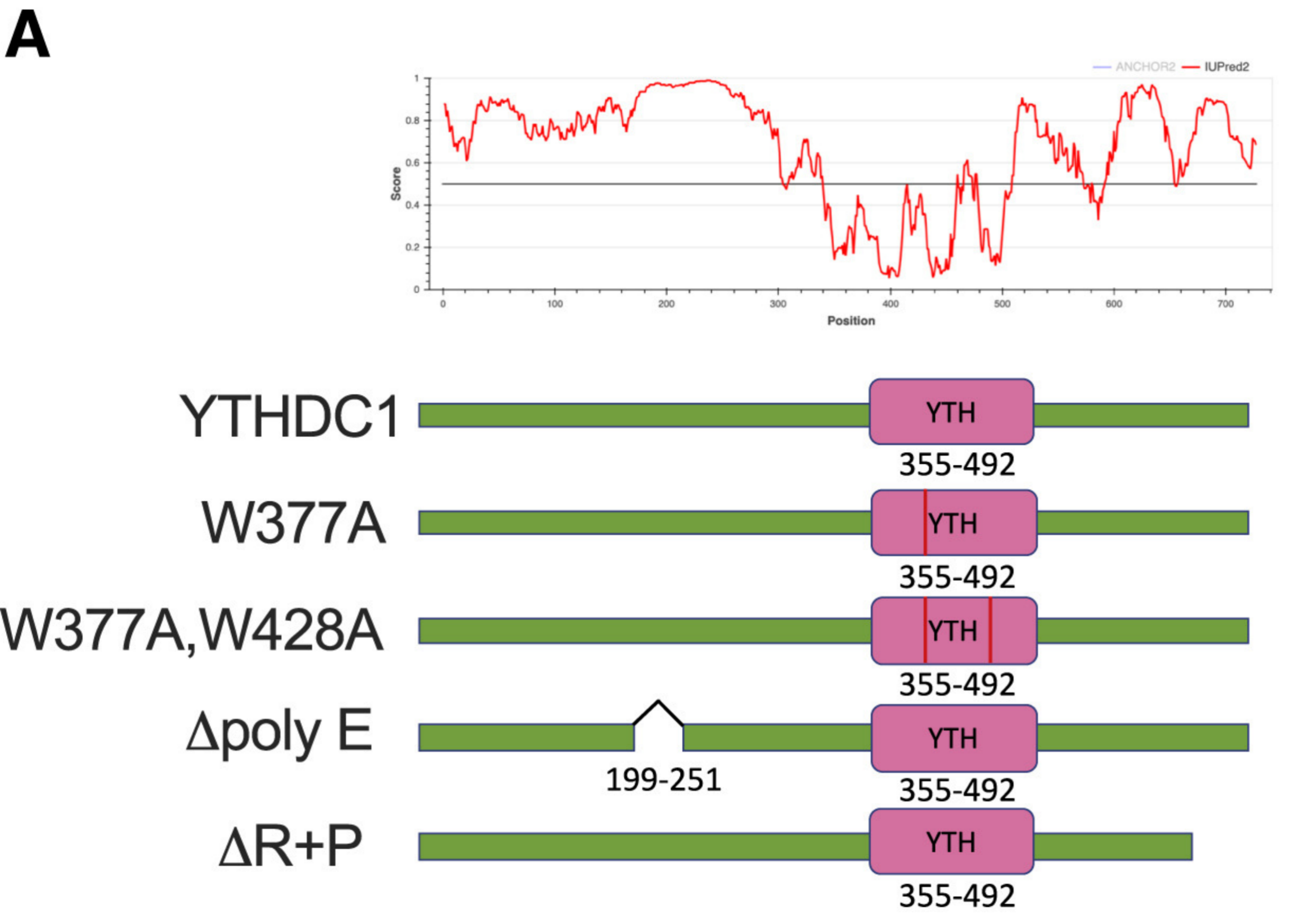
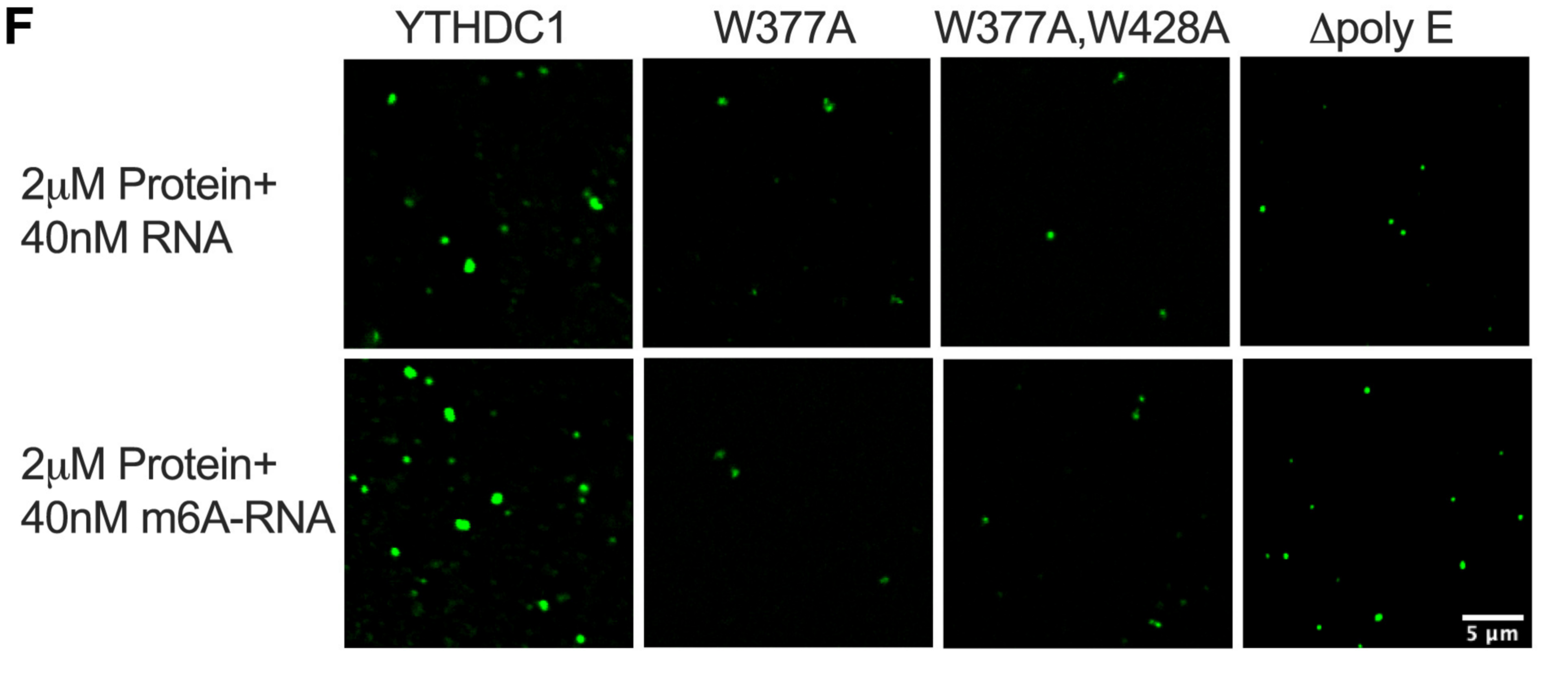
Products and services related to "phase separation research:
1. Gene knockout customization service: Large fragment/precise/non-precise knockout for the customer-specified area (coding area/non-coding area);
2. Inducible shRNA knockdown stable cell lines: For essential genes, we provide inducible knockdown stable cell line protocols;
3. Construction of stable cell lines by in situ insertion of gene taggingBased on dTAG precise targeting protein degradation, real-time monitoring of protein function;
4. Construction of stable cell lines by in situ insertion of gene tagging: EGFP,RFP,Strep-tag and other tags are inserted into the N-terminal/C-terminal of the gene in situ;
5. Construction of point mutation stable cell lineSite-directed mutagenesis of the amino acids of the gene specified by the customer to construct a stable cell line.
2. Phase separation is involved in DNA damage and repair
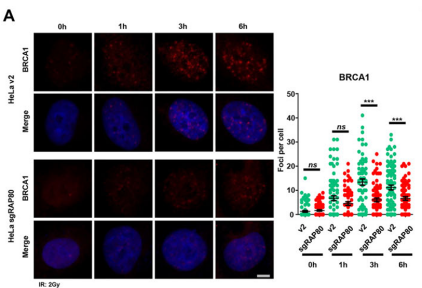
Researchers have revealed a new mechanism for RAP80-mediated recruitment of BRCA1 [4], providing new insights into the role of phase separation in DNA double-strand break repair. The binding of RAP80 to the Lys63-linked polyubiquitin chain increases the multivalent interaction, thereby inducing the liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of RAP80 at the site of DNA damage. At the same time, it was found that RAP80 LLPS enhanced the radiation resistance of tumor cells, indicating that RAP80 may be a potential target for tumor radiotherapy.
The study was adoptedCRISPR Knockout RAP80It is proved that it forms a liquid condensate in the nucleus, and the elimination of RAP80 agglutination significantly inhibits the formation of BRCA1 focus, revealing the key role of RAP80 agglutination in BRCA1 recruitment and radiation sensitivity.
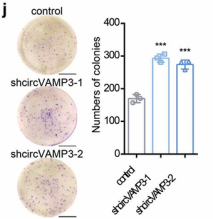
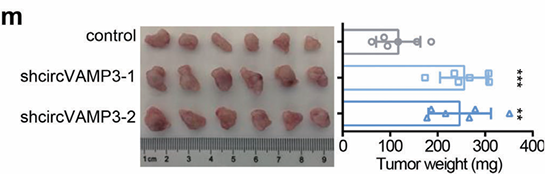
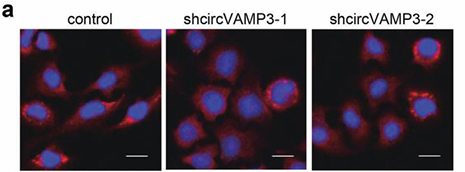
1) through gene editing inknockdown circVAMP3 in cells and miceIt is proved that it can inhibit the proliferation and migration of HCC cells.
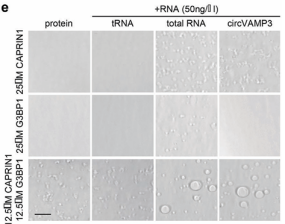
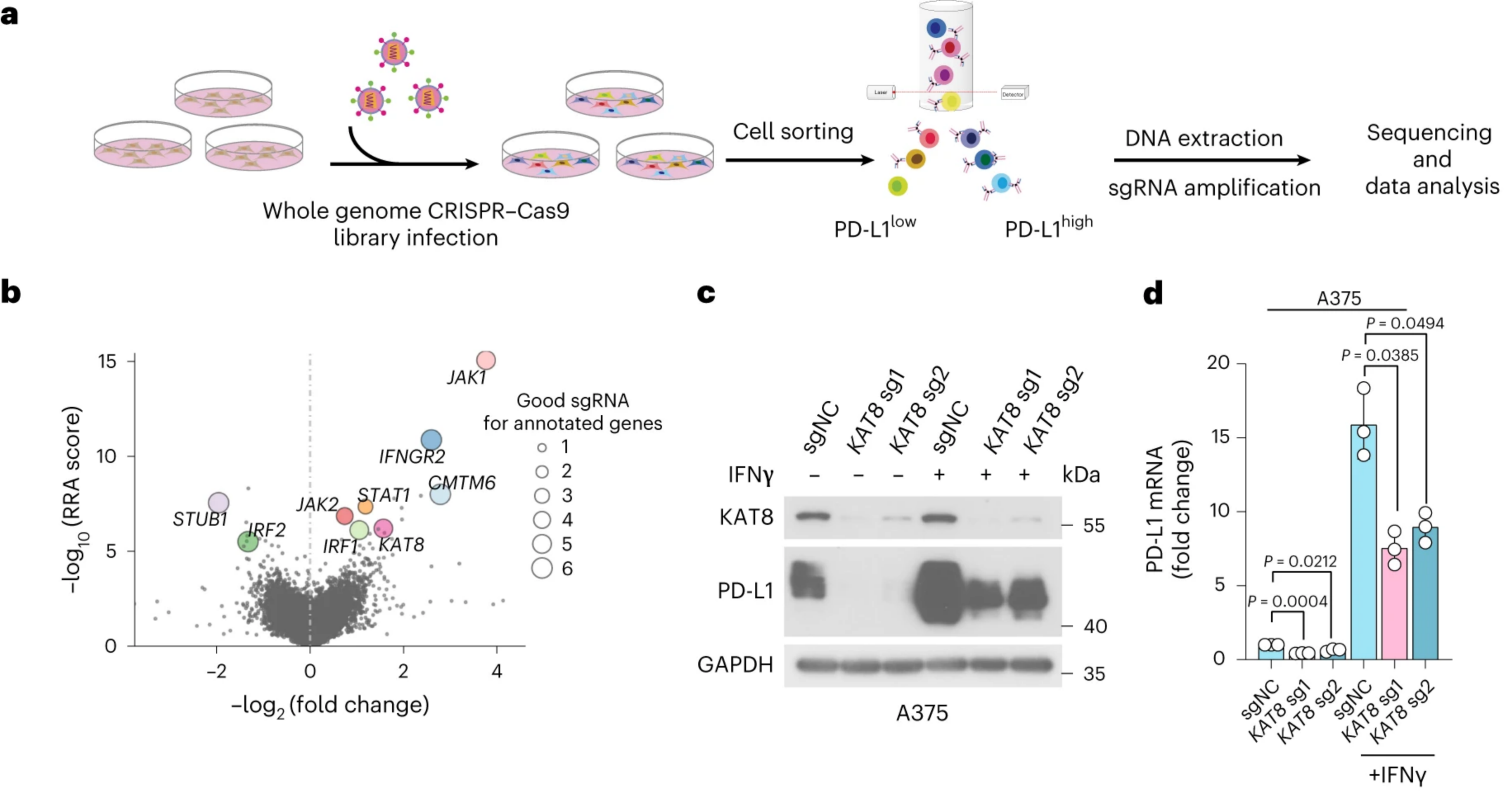
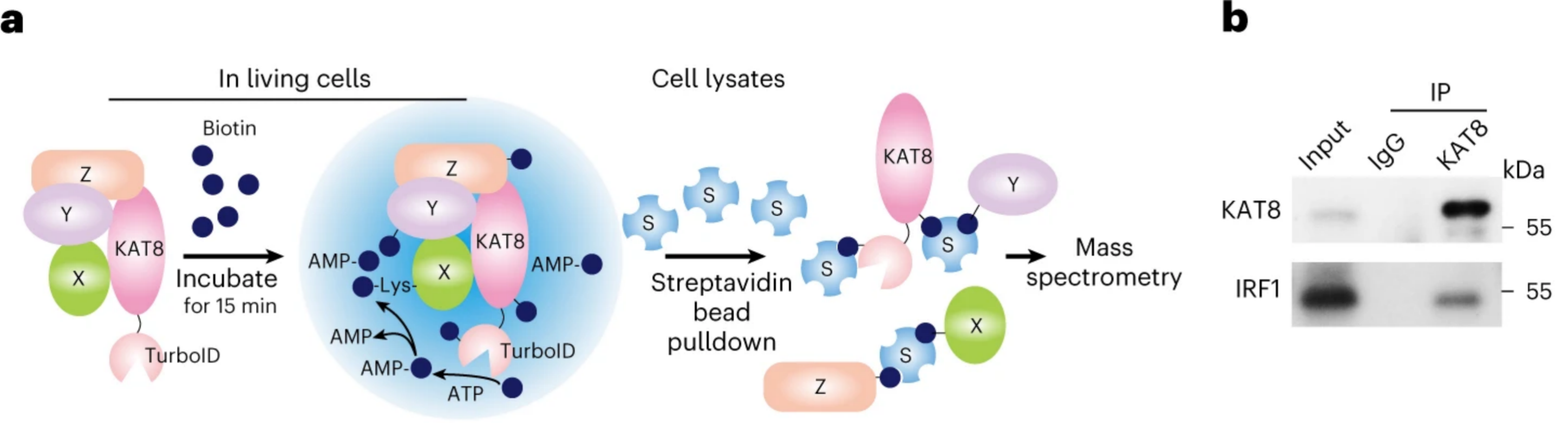
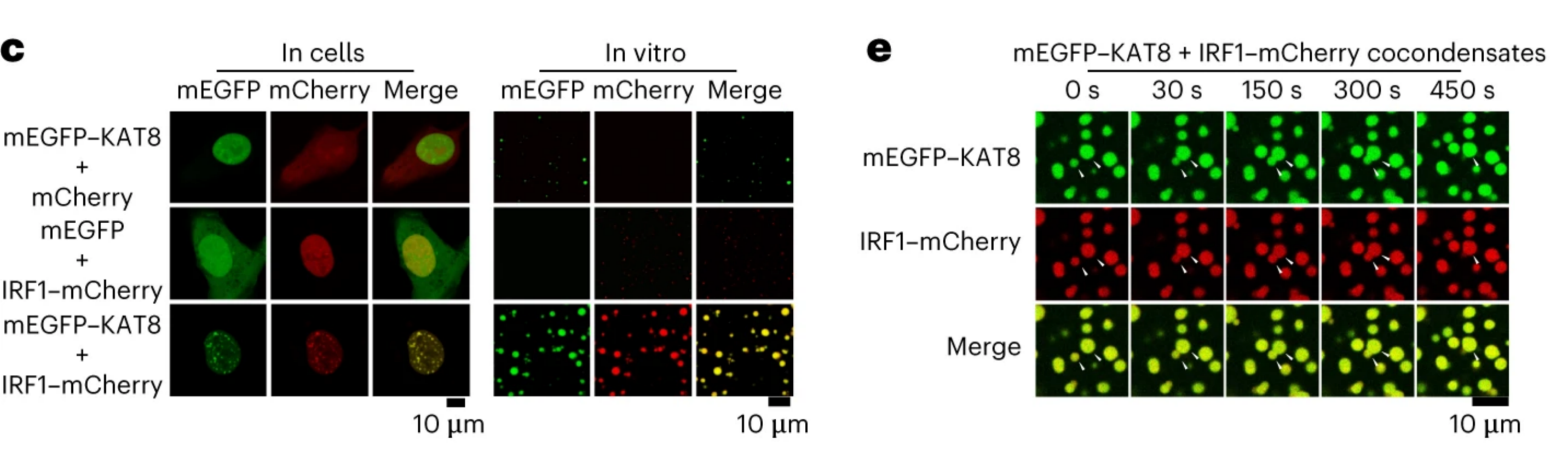
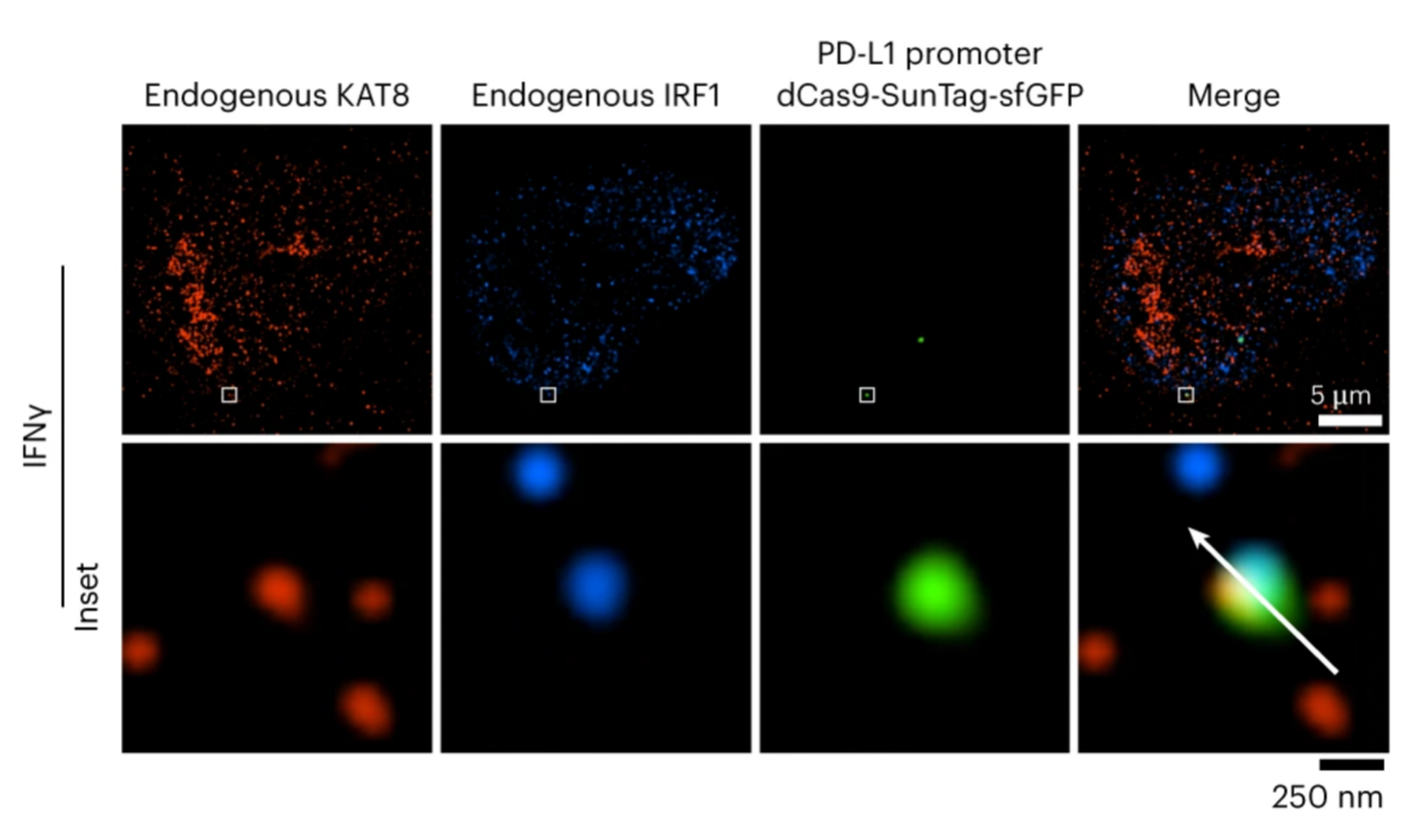
4) UtilizationdCas9-SunTag-sgARRAYConducting genomic mapping, the researchers observed that endogenous KAT8-IRF1 aggregates can be localized to the PD-L1 promoter.
Products and services related to "phase separation research:
1. Whole genome gene knockout mixed pooled library screening:Greater throughput and less time-consuming, suitable for phenotypes that can be changed by selective pressure, such as cell viability/proliferation assays or FACS analysis;
2. Screening of human/mouse gene knockout array arrayed library: For 19 metabolic pathways, higher accuracy, simplified data interpretation, strong experimental repeatability, and broader research needs;
3. Construction of stable cell lines by in situ insertion of gene tagging:Gene in situ N-terminal/C-terminal insertion of EGFP,mCherry and other tags for co-localization studies;
4. Construction of stable cell lines by in situ insertion of gene tagging:The gene is inserted into birID at the N-terminal/C-terminal in situ, and TurboID and other tags are used for adjacent labeling detection, which can find protein-protein interaction (weak interaction, transient interaction); Strep-tag and other tags are inserted in situ for AP-MS detection, which can find strong protein-protein interaction;
5. Granular manstrep II purified packingVery high affinity enrichment (100-fold higher than antibody enrichment) for Strep-tag proteins as well as biotin-labeled proteins.
6. AP-MS/IP-MS detection: Mass spectrometry detection of cell samples adjacent to the label or affinity label (Strep-tag) to find interacting proteins;
7. Construction of stable cell lines by in situ insertion of gene tagging:Live cell imaging analysis of genomic loci dCas9-SunTag the system and fluorescent proteins.
The importance of 3. gene editing technology in phase separation research
Gene editing at the cellular level in vitro (knock-out/knock-in) has become a regular technique in phase separation studies. Biological studies on phase separation, as well as in cancer, have played a key role. With the further development of phase separation research, it will also lead to the further integration of gene editing technology in this field.
As a technology-driven company focusing on the development of high-throughput gene editing tools, Graneman Bio will continue to focus on this field and launch related products and services to comprehensively assist researchers in phase separation research!
References
2024 /
08-04
Classification:
Company News
Related Information

