Culture and editing of THP-1 cell line of Yiye Zhiqiu I
2024-09-24
Welcome to pay attention to Elem.The "Yiye Zhiqiu" series saw a high-level scientific research paper through a high-quality gene editing cell line. In the promotion of "the glory of the king" in the field of scientific research and academic research, strive to find your own "one leaf knows autumn"! "Glory is never the glory of one person"!
1. Cell background
THP-1 cell line was isolated from the peripheral blood of a 1-year-old boy with acute monocytic leukemia [1]. Since its establishment in 1980, THP-1 cells have been widely used in the study of monocyte and macrophage-related mechanisms, signaling pathways, nutrition and drug delivery. Compared with U937, HL-60, ML-2 and other leukemia cell lines, THP-1 have more similar morphological and functional characteristics (including cell differentiation markers) of human primary monocytes. Compared with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC),THP-1 is easier to be cultured and amplified in the laboratory, and has a more stable gene background, and there is no individual difference of PBMC, which is conducive to the reproduction of experimental results [2]. Therefore, THP-1 is a commonly used acute monocytic leukemia cell line in major laboratories and is an ideal tool for studying immunity and inflammation.
2. Cell description
Species: human; Tissue: peripheral blood; Cell morphology: suspension growth, monocytes; Cell doubling time:~ 30-48 hours; Culture conditions: complete medium composition: RPMI-1640 + 10% FBS +0.05 mM β-mercaptoethanol + 1% P/S; Culture environment: 37 ℃, 5% CO2; Subculture ratio: 1:2~1:4; Subculture frequency: once every 2~3 days.
The normal morphology of THP-1 mononuclear cells is small and bright round cells in suspension, with a few clusters forming grape-like, full grains and clear contours. The cells grow faster in an acidic environment, so when the culture medium turns yellow slightly (orange red), it is more suitable for cell growth, and fluid replacement or semi-fluid replacement is sufficient at this time. After opening the 1640 culture medium, long-term storage pH will be high, it is recommended to use it within one week after opening. The cells have high requirements for serum, and the difference in serum quality may cause changes in cell status. It is recommended to use high-quality fetal bovine serum.
3. Cell morphology
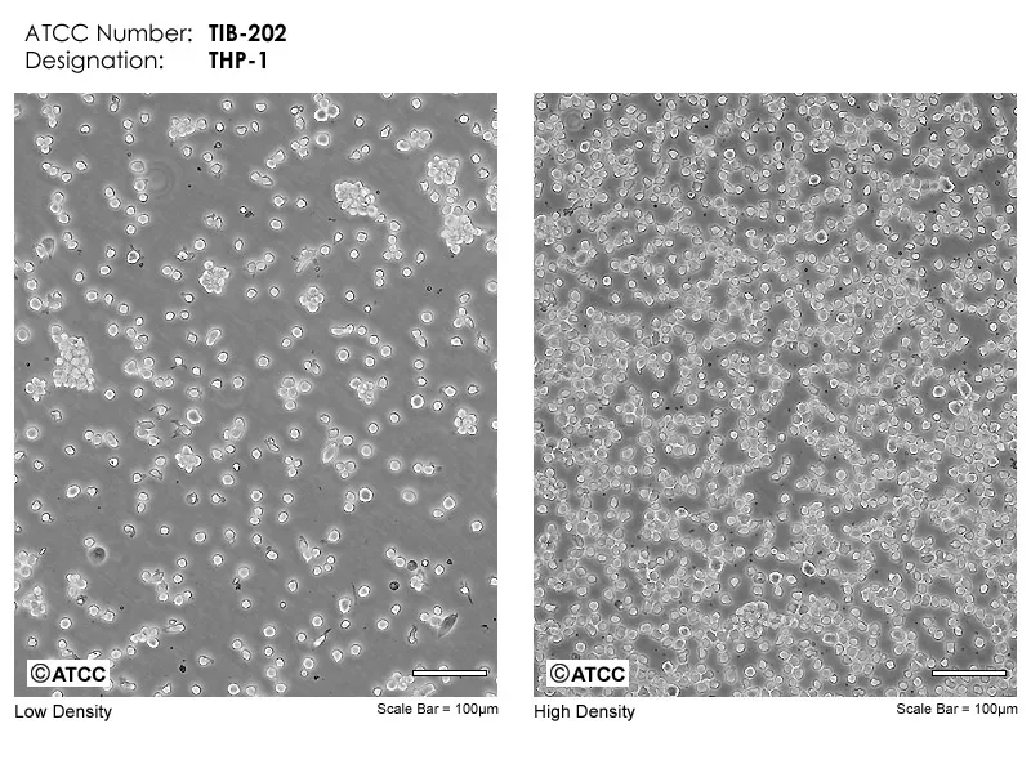
Figure 1 Reference normal morphology of THP-1 cell ATCC
4. Frequently Asked Questions
4.1 THP-1 adherence problem
A small amount of cell adherence during THP-1 cell culture is normal (Figure 2) and is not a concern. The cells can be collected by gentle blowing or the adherent portion of the cells discarded.
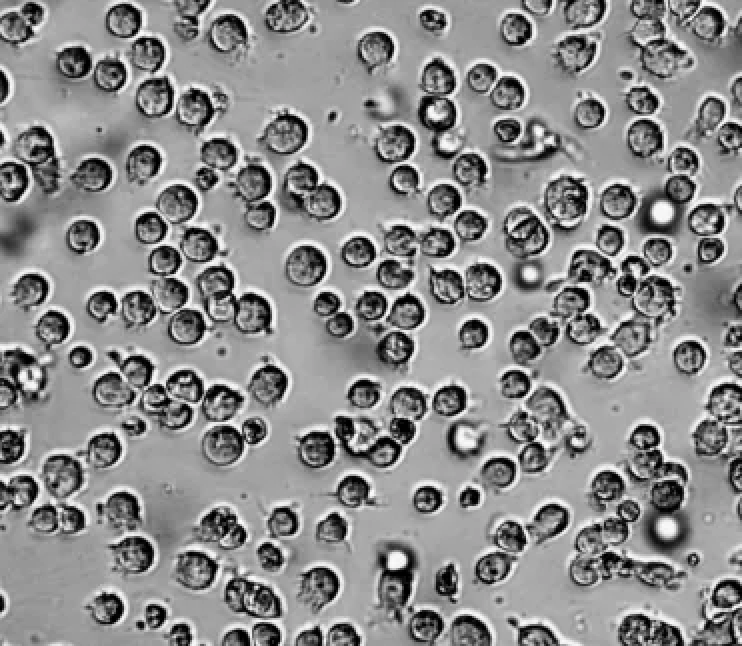
FigureA small amount of 2 THP-1 cells adhered to the wall
It is normal for a small number of cells to stick to the wall. Transfer the cell suspension to a new bottle. When the proportion of adherent cells was higher20% (Figure 3), indicating that the cell growth environment is abnormal, and it is necessary to check whether the incubator setting, culture medium composition and culture vessel are abnormal.
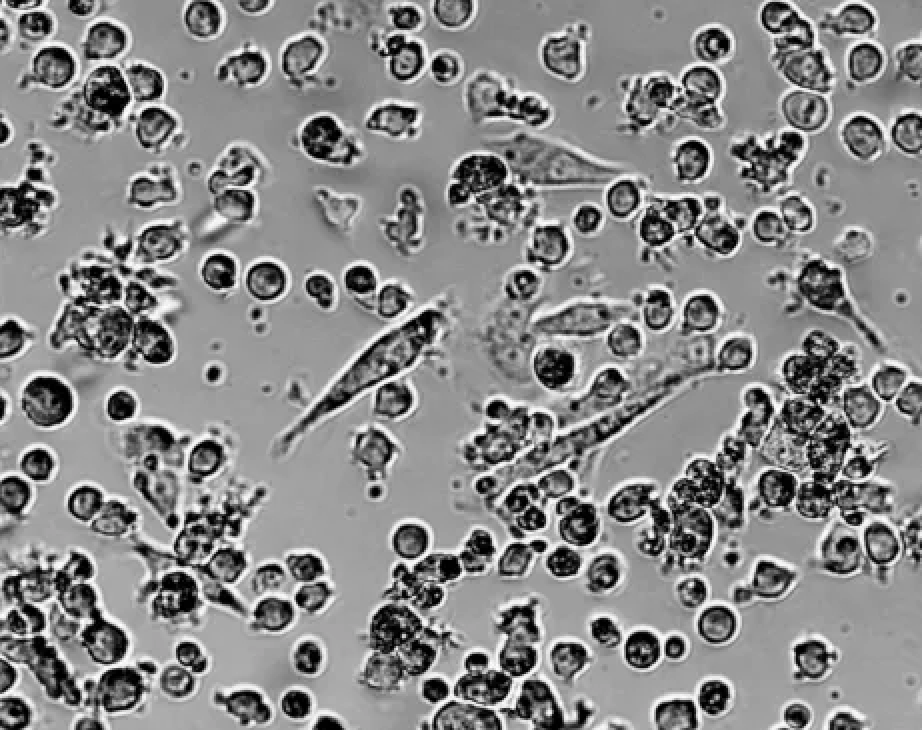
Figure3 A large number of THP-1 cells attached to the wall
4.2 THP-1 clustering problem
A small number of cell clusters, in the shape of grape clusters, are normal (Fig.4), especially when the cell density is low, this situation is easy to occur. Changing the brand of serum or increasing the proportion of serum (no more than 20%) can help solve the problem of agglomeration. It is not recommended to blow away the aggregated cells, and when the density is high, they will disperse themselves.
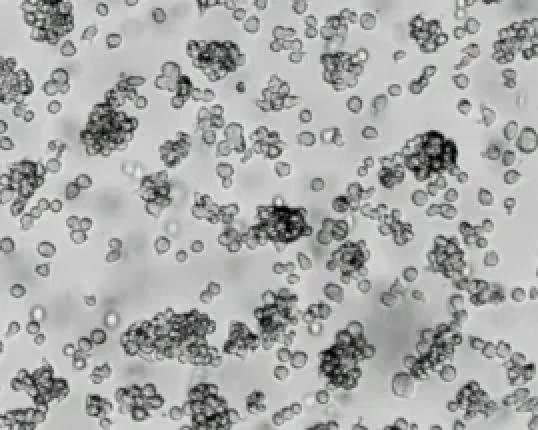
Figure4 THP-1 cell aggregates
4.3 THP-1 not recover
Affected by transport, suspension cells will transiently appear morphological changes, such as pseudopodia. through subculture,About 1 week can return to normal. Some cells die during transit to produce debris that can be removed by passage centrifugation.
DueTHP-1 are suspended cells, which are more susceptible to cryopreservation. It is recommended to increase the density of cryopreservation, 5*10 ^ 6-10 ^ 7/ml, in order to improve the survival rate of recovery. In addition can be usedNoneDMSO cryopreservation solution(Consulting Elem Sales)Improve cell viability.
4.4 THP-1 difficulties in gene editing
THP-1 is a near-tetraploid suspension cell, and the positive rate of regular gene editing methods (such as slow virus method, plasmid method, etc.) in THP-1 is very low. CRISPR/Cas9 is favored for gene editing applications due to its ease of construction, high efficiency, and low toxicity in human cells. The unique strategy of targeting multiple sgRNAs in early exons of Elem organisms can significantly increase the loss of large fragments in addition to the frameshift mutations caused by traditional NHEJ DNA repair, thereby greatly increasing the efficiency of gene knockout.
THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia cell lines, whether viral vectors, DNA plasmids, or in vitro transcription tracrRNA, traditional gene editing reagents inevitably activate the DNA/RNA sensing pathway in cells to a certain extent, leading to cell apoptosis. Elem biological selection uses chemically modified synthetic sgRNA to reduce the activation of RIG-I and type I interferon pathways, thereby maximizing cell survival and ensuring that the phenotype of edited cells is not affected by the activation of type I interferon pathways. The RNP was delivered into the cell by simple electrotransformation, and targeted gene editing was completed in 3 days.
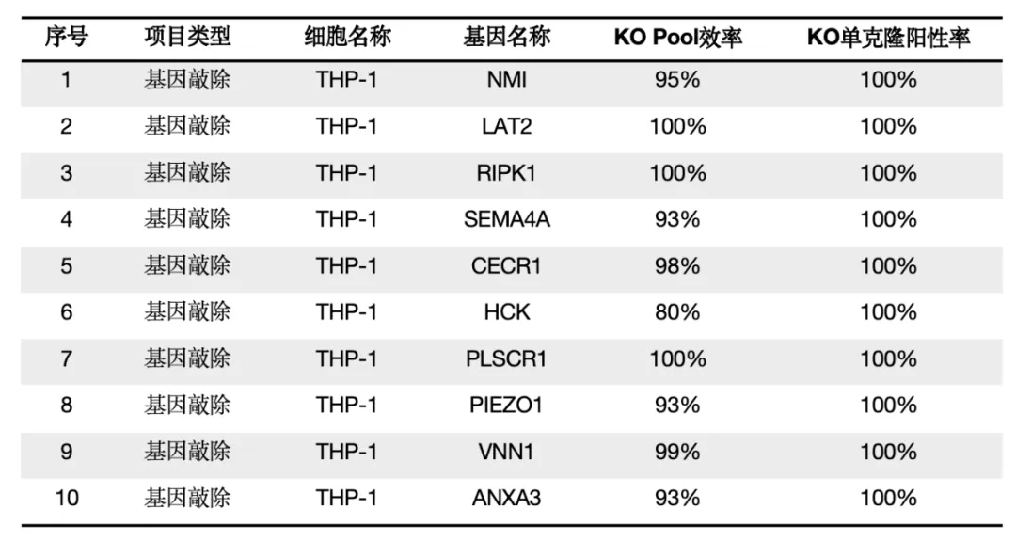
The following is the biological part of the Elem.THP-1 cell gene knockout cases and in stock cell lines (consult Elem to purchase in stock cell lines or custom THP-1 knockout cell lines)
References
[1] Chanput W, Mes J J, Wichers H J. THP-1 cell line: an in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach[J]. International immunopharmacology, 2014, 23(1): 37-45.
[2] Benyoucef A, Marchitto L, Touzot F. CRISPR gene-engineered CYBBko THP-1 cell lines highlight the crucial role of NADPH-induced reactive oxygen species for regulating inflammasome activation[J]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 2020.
2024 /
09-24
Classification:
Industry News
Related Information

